As a result of these activities, Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań, the Centre for Theoretical Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Theoretical and Applied Informatics of the Polish Academy of Sciences, and the National Centre for Nuclear Research (NCBJ) in Świerk have already become institutional members of the IBM Quantum Network. Several new teams from Polish universities plan to complete the first phase of experiments in close collaboration with the PSNC. In addition, a number of experiments have been carried out as part of the R&D work carried out directly by the PSNC teams using the largest real IBM Q quantum computers. Different approaches and new quantum methods have been tested, including experimentally investigating the impact of using different types of quantum optimisation algorithms – QAOA (Quantum Approximate Optimisation Algorithm), Quantum Optimisation Optimisation Approach and QAOA with Educated Guess strategy. The results demonstrated the applicability of quantum algorithms in solving test optimisation problems, such as task serialisation problems, and the use of quantum algorithms in complex air traffic safety management problems.
As part of the remote use of the physical resources of IBM Q quantum computers available through the IBM Quantum Innovation Center, the Center for Theoretical Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences has developed an effective method for characterising readout errors. Currently, readout errors contribute significantly to the overall noise affecting the performance of available quantum computers, and full characterisation of the overall readout noise is not feasible for devices consisting of a large number of qubits. The new method proposed by the Centre for Theoretical Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences is efficient because it scales logarithmically with the number of qubits, so it can be used to characterise the measurement errors of quantum devices consisting of many qubits. The new method has been successfully implemented and used experimentally to characterise the measurement errors of the 127-qubit IBM Q quantum computers Cusco, Sherbrooke, Brisbane and Nazca. The results obtained allow the construction of a correlated measurement error model, and the reconstructed measurement error models were used to perform an error mitigation procedure.
PCSS Energy Lab: Energy Transformation of Eastern Wielkopolska
2025-07-10
Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center (PCSS) has launched a five-year scientific project aimed at supporting the energy transformation of eastern Wielkopolska (Greater Poland). As a part of the research, "digital twins" of buildings and locations in the region will be created, allowing for simulations. The project consists of three components: the Digital Twin Laboratory, the RES (Renewable Energy Sources) Laboratory, and the Living Lab.
OSCARS: Paving the Way for Open Science in the European Research Area
2025-07-03
The European scientific landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by initiatives such as OSCARS. This ambitious, four-year Horizon Europe project aims to revolutionize research practices across the continent by promoting Open Science principles and supporting the widespread adoption of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) data. Our Centre has just joined OSCARS through the DARIAH-EU consortium. PCSS will focus on Work Package 2.
Poland Announces Its Participation in the EU’s AI Gigafactories Program
2025-06-12
The Polish Ministry of Digital Affairs has announced that Poland is finalizing discussions with European Union partners regarding its participation in the EU's AI Gigafactory building program. Following the conclusion of public consultations, a formal application is expected to be submitted to EU structures before 20 June 2025.
One Logo, One Name – Even More Possibilities
2025-06-02
We are pleased to announce that official name of our Center has just been unified. Henceforth, the one name that represents us globally is PCSS.
Introduction to Knowledge Graphs – The Very First GRAPHIA Webinar
2025-05-20
We are pleased to invite you to the first GRAPHIA webinar, which is going to take place on 13 June 2025 at 11:00 CEST. The online session’s title is “Introduction to Knowledge Graphs” and it will be hosted by Julien Homo.
LUMEN Is Waiting for You Online!
2025-05-20
The LUMEN (Linked User-Driven Multidisciplinary Exploration Network) project was born of cross-domain collaboration among: mathematics, social sciences and humanities (SSH), earth system and molecular dynamics. As one of the project’s partners, PSNC is proud to present LUMEN’s official website, which has recently made its online debut!
Support Cultural Heritage – Take Part in a Short 3D-4CH Survey 🙂
2025-04-30
3D-4CH is a European project the goal of which is to revolutionize the way cultural heritage is protected, digitized, and made accessible through the use of advanced 3D technologies, artificial intelligence, and extended reality. Now you can also contribute to saving the precious cultural heritage for the next generations. Just take a short survey aimed at individuals, companies, and institutions that conduct courses or workshops related to the digitization of cultural heritage. The deadline for completing this survey is 21 May 2025.
PSNC is a part of Nomios and Nokia’s Connecting Europe Tour
2025-04-24
"The Connecting Europe Tour" is a video-blog project presented by Nomios and Nokia. Nat and Fraser, two young and witty entrepreneurs are on an exciting journey across Europe to dive into the world of cutting-edge technology and innovation. Throughout the mini series the guys visit: London, Cambridge, Paris, Brussels, Amsterdam, Geneva, Berlin and Poznań – where they explore the backbone of European research and education, the GÉANT network.
Fifth Edition of the European Quantum Systems and Software Summit at PCSS
2025-06-27
Following a successful series of European Quantum Systems and Software Summits (EQS3) over the past three years, the fifth edition of this event was held in Poznań. This year's three-day meeting (25-27 June) was co-organized by a renowned quantum expert dr. hab. inż. Krzysztof Kurowski with the support of the Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center (PCSS). EQS3 is a closed conference, aimed at the European scientific community and its international partners, with the primary goal of further shaping a common vision and strategy for the development of European quantum and hybrid systems.
PCSS Is a Partner of the “Quantum Babylon” Exhibition
2025-06-27
We are thrilled to announce our institutional partnership with the "Quantum Babylon" exhibition, currently on display at the National Museum in Szczecin. The vernissage, held on 26 June 2025, drew not only contemporary art enthusiasts and admirers of Roman Lipski's work, but also an international group of experimentalists who harness modern technologies to create new dimensions in art & science.
Innovative Space Research: Inauguration of the LOFAR ERIC Project at PCSS
2025-06-26
On 25 June 2025, PCSS hosted a special meeting of POLFAR, combined with the opening of the LOFAR ERIC European Research Infrastructure Consortium's operations in Poland. Among the guests were representatives from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, the Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the SOLARIS National Synchrotron Radiation Centre, ESO, CTAO ERIC, and, of course, members of the POLFAR consortium, including PCSS.
The Launch of the First Polish AI Factory – PIAST-AI
2025-06-23
Today at PCSS a significant step towards making Europe a leader in AI technology has been taken. The PIAST-AI Factory at the Poznań Center was selected by the European Commission to participate in the "AI Factories" program. This makes the Capital of Wielkopolska region a crucial driving force in the development of fields such as: IT, cybersecurity, space technologies, robotics, and sustainable development.
Inauguration of PIAST-Q – A Leap for European Quantum Computing
2025-06-23
Today, under the Polish Presidency of the Council of the European Union, EuroHPC JU inaugurated PIAST-Q in Poznań (Poland). This first inauguration of a EuroHPC quantum computer marks a milestone in building a European quantum computing infrastructure. This is also the first EuroHPC infrastructure located in Poland.
DARIAH Annual Event 2025: The Future of Digital Humanities in Göttingen
2025-06-21
From 17 to 20 June 2025, the prestigious DARIAH Annual Event 2025 took place in Göttingen (Germany). The Göttingen State and University Library was chosen as the venue for this event, gathering experts and enthusiasts of digital humanities from all over Europe, including representatives of PCSS. The first day was dedicated to internal DARIAH meetings, while the main part of the conference ran from 18 to 20 June.
Digital Summit in Gdańsk
2025-06-19
On 17 and 18 June 2025, the Digital Summit conference was held at the European Solidarity Centre in Gdańsk. This event created a space for discussion on Europe's digital future, involving ministers, technology industry leaders, scientists, and representatives of the most innovative companies; Robert Pękal, the Director of PCSS, was among them. During the conference, Poland's presidency of the EU Council in the area of digitalization was summarized, and common plans for this area of activity for the coming years were outlined.
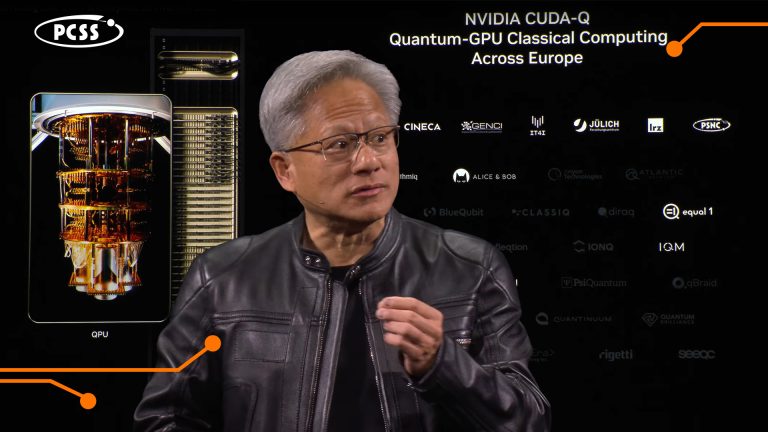
PCSS Quantum Technologies at NVIDIA GTC in Paris
2025-06-17
At the NVIDIA GTC AI conference for developers in Paris (10-12 June 2025), the PCSS’ name appeared among the leading European institutions in the realm of quantum computing during the speech of the NVIDIA co-founder and CEO, Jensen Huang.
About PSNC in GÉANT CONNECT
2025-06-10
The latest, June issue of the magazine "CONNECT", focused on the GÉANT network and community, features an article on next-generation research infrastructures. These projects are being implemented within four leading projects run by PCSS and based on the PIONIER Network.
“Long-Distance Coherent Quantum Communications in Deployed Telcom Networks” – Piotr Rydlichowski in Nature Magazine
2025-04-24
The newest issue of Nature magazine (04/2025) features an article titled “Long-Distance Coherent Quantum Communications in Deployed Telcom Networks” and one of its coauthors is Piotr Rydlichowski – a PSNC’s researcher from the Centre’s Network Technologies Division.
GÉANT’s “Foresight 2030: Navigating Change” Report
2025-01-08
At the end of 2024, GÉANT released a report identifying the key opportunities and challenges facing the NREN community (National Research and Education Network) in the coming decade. One of the authors of this document is Raimundas Tuminauskas – Head of the Network Infrastructure and Services Department at PSNC.
Nobel Prizes 2024: AI in Physics and Chemistry
2024-10-17
This year's Nobel Prizes in Physics and Chemistry highlight the groundbreaking role of artificial intelligence in those fields. To get insights into this significant development, we reached out to Dr Mikołaj Buchwald – an expert from the PSNC Internet Services Department, whose research interests include cognitive neuroscience, machine learning methodology, as well as using AI plus advanced data analysis to explain human physiology and psychology.
PSNC Leaps into the future of computing
2024-09-04
Thanks to the Dariah.lab infrastructure, the first pilot projects for the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage resources have been implemented in 2023. Dariah.lab is a research infrastructure for the humanities and arts, built as part of the DARIAH-PL project. It serves to acquire, store and integrate cultural data from the humanities and social sciences, and to process, visualise and share digital resources.
International Media on PSNC
2024-09-03
Here is a short sellection of recent articles on PSNC that have appeared in some international media.
Dariah.lab: cultural heritage documentation
2024-04-19
Thanks to the Dariah.lab infrastructure, the first pilot projects for the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage resources have been implemented in 2023. Dariah.lab is a research infrastructure for the humanities and arts, built as part of the DARIAH-PL project. It serves to acquire, store and integrate cultural data from the humanities and social sciences, and to process, visualise and share digital resources.
Experiments using the largest IBM Q quantum computers
2024-04-14
The Polish Quantum Computing Node established at the Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center - IBM Quantum Innovation Center - focused its activities in 2023 on expanding partnerships with leading centers and teams dealing with the development of quantum algorithms and their potential applications.
PCSS Energy Lab: Energy Transformation of Eastern Wielkopolska
2025-07-10
Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center (PCSS) has launched a five-year scientific project aimed at supporting the energy transformation of eastern Wielkopolska (Greater Poland). As a part of the research, "digital twins" of buildings and locations in the region will be created, allowing for simulations. The project consists of three components: the Digital Twin Laboratory, the RES (Renewable Energy Sources) Laboratory, and the Living Lab.
Fifth Edition of the European Quantum Systems and Software Summit at PCSS
2025-06-27
Following a successful series of European Quantum Systems and Software Summits (EQS3) over the past three years, the fifth edition of this event was held in Poznań. This year's three-day meeting (25-27 June) was co-organized by a renowned quantum expert dr. hab. inż. Krzysztof Kurowski with the support of the Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center (PCSS). EQS3 is a closed conference, aimed at the European scientific community and its international partners, with the primary goal of further shaping a common vision and strategy for the development of European quantum and hybrid systems.
About PSNC in GÉANT CONNECT
2025-06-10
The latest, June issue of the magazine "CONNECT", focused on the GÉANT network and community, features an article on next-generation research infrastructures. These projects are being implemented within four leading projects run by PCSS and based on the PIONIER Network.
OSCARS: Paving the Way for Open Science in the European Research Area
2025-07-03
The European scientific landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by initiatives such as OSCARS. This ambitious, four-year Horizon Europe project aims to revolutionize research practices across the continent by promoting Open Science principles and supporting the widespread adoption of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) data. Our Centre has just joined OSCARS through the DARIAH-EU consortium. PCSS will focus on Work Package 2.
PCSS Is a Partner of the “Quantum Babylon” Exhibition
2025-06-27
We are thrilled to announce our institutional partnership with the "Quantum Babylon" exhibition, currently on display at the National Museum in Szczecin. The vernissage, held on 26 June 2025, drew not only contemporary art enthusiasts and admirers of Roman Lipski's work, but also an international group of experimentalists who harness modern technologies to create new dimensions in art & science.
“Long-Distance Coherent Quantum Communications in Deployed Telcom Networks” – Piotr Rydlichowski in Nature Magazine
2025-04-24
The newest issue of Nature magazine (04/2025) features an article titled “Long-Distance Coherent Quantum Communications in Deployed Telcom Networks” and one of its coauthors is Piotr Rydlichowski – a PSNC’s researcher from the Centre’s Network Technologies Division.
Poland Announces Its Participation in the EU’s AI Gigafactories Program
2025-06-12
The Polish Ministry of Digital Affairs has announced that Poland is finalizing discussions with European Union partners regarding its participation in the EU's AI Gigafactory building program. Following the conclusion of public consultations, a formal application is expected to be submitted to EU structures before 20 June 2025.
Innovative Space Research: Inauguration of the LOFAR ERIC Project at PCSS
2025-06-26
On 25 June 2025, PCSS hosted a special meeting of POLFAR, combined with the opening of the LOFAR ERIC European Research Infrastructure Consortium's operations in Poland. Among the guests were representatives from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, the Space Research Centre of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the SOLARIS National Synchrotron Radiation Centre, ESO, CTAO ERIC, and, of course, members of the POLFAR consortium, including PCSS.
GÉANT’s “Foresight 2030: Navigating Change” Report
2025-01-08
At the end of 2024, GÉANT released a report identifying the key opportunities and challenges facing the NREN community (National Research and Education Network) in the coming decade. One of the authors of this document is Raimundas Tuminauskas – Head of the Network Infrastructure and Services Department at PSNC.
One Logo, One Name – Even More Possibilities
2025-06-02
We are pleased to announce that official name of our Center has just been unified. Henceforth, the one name that represents us globally is PCSS.
The Launch of the First Polish AI Factory – PIAST-AI
2025-06-23
Today at PCSS a significant step towards making Europe a leader in AI technology has been taken. The PIAST-AI Factory at the Poznań Center was selected by the European Commission to participate in the "AI Factories" program. This makes the Capital of Wielkopolska region a crucial driving force in the development of fields such as: IT, cybersecurity, space technologies, robotics, and sustainable development.
Nobel Prizes 2024: AI in Physics and Chemistry
2024-10-17
This year's Nobel Prizes in Physics and Chemistry highlight the groundbreaking role of artificial intelligence in those fields. To get insights into this significant development, we reached out to Dr Mikołaj Buchwald – an expert from the PSNC Internet Services Department, whose research interests include cognitive neuroscience, machine learning methodology, as well as using AI plus advanced data analysis to explain human physiology and psychology.
Introduction to Knowledge Graphs – The Very First GRAPHIA Webinar
2025-05-20
We are pleased to invite you to the first GRAPHIA webinar, which is going to take place on 13 June 2025 at 11:00 CEST. The online session’s title is “Introduction to Knowledge Graphs” and it will be hosted by Julien Homo.
Inauguration of PIAST-Q – A Leap for European Quantum Computing
2025-06-23
Today, under the Polish Presidency of the Council of the European Union, EuroHPC JU inaugurated PIAST-Q in Poznań (Poland). This first inauguration of a EuroHPC quantum computer marks a milestone in building a European quantum computing infrastructure. This is also the first EuroHPC infrastructure located in Poland.
PSNC Leaps into the future of computing
2024-09-04
Thanks to the Dariah.lab infrastructure, the first pilot projects for the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage resources have been implemented in 2023. Dariah.lab is a research infrastructure for the humanities and arts, built as part of the DARIAH-PL project. It serves to acquire, store and integrate cultural data from the humanities and social sciences, and to process, visualise and share digital resources.
LUMEN Is Waiting for You Online!
2025-05-20
The LUMEN (Linked User-Driven Multidisciplinary Exploration Network) project was born of cross-domain collaboration among: mathematics, social sciences and humanities (SSH), earth system and molecular dynamics. As one of the project’s partners, PSNC is proud to present LUMEN’s official website, which has recently made its online debut!
DARIAH Annual Event 2025: The Future of Digital Humanities in Göttingen
2025-06-21
From 17 to 20 June 2025, the prestigious DARIAH Annual Event 2025 took place in Göttingen (Germany). The Göttingen State and University Library was chosen as the venue for this event, gathering experts and enthusiasts of digital humanities from all over Europe, including representatives of PCSS. The first day was dedicated to internal DARIAH meetings, while the main part of the conference ran from 18 to 20 June.
International Media on PSNC
2024-09-03
Here is a short sellection of recent articles on PSNC that have appeared in some international media.
Support Cultural Heritage – Take Part in a Short 3D-4CH Survey 🙂
2025-04-30
3D-4CH is a European project the goal of which is to revolutionize the way cultural heritage is protected, digitized, and made accessible through the use of advanced 3D technologies, artificial intelligence, and extended reality. Now you can also contribute to saving the precious cultural heritage for the next generations. Just take a short survey aimed at individuals, companies, and institutions that conduct courses or workshops related to the digitization of cultural heritage. The deadline for completing this survey is 21 May 2025.
Digital Summit in Gdańsk
2025-06-19
On 17 and 18 June 2025, the Digital Summit conference was held at the European Solidarity Centre in Gdańsk. This event created a space for discussion on Europe's digital future, involving ministers, technology industry leaders, scientists, and representatives of the most innovative companies; Robert Pękal, the Director of PCSS, was among them. During the conference, Poland's presidency of the EU Council in the area of digitalization was summarized, and common plans for this area of activity for the coming years were outlined.
Dariah.lab: cultural heritage documentation
2024-04-19
Thanks to the Dariah.lab infrastructure, the first pilot projects for the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage resources have been implemented in 2023. Dariah.lab is a research infrastructure for the humanities and arts, built as part of the DARIAH-PL project. It serves to acquire, store and integrate cultural data from the humanities and social sciences, and to process, visualise and share digital resources.
PSNC is a part of Nomios and Nokia’s Connecting Europe Tour
2025-04-24
"The Connecting Europe Tour" is a video-blog project presented by Nomios and Nokia. Nat and Fraser, two young and witty entrepreneurs are on an exciting journey across Europe to dive into the world of cutting-edge technology and innovation. Throughout the mini series the guys visit: London, Cambridge, Paris, Brussels, Amsterdam, Geneva, Berlin and Poznań – where they explore the backbone of European research and education, the GÉANT network.
PCSS Quantum Technologies at NVIDIA GTC in Paris
2025-06-17
At the NVIDIA GTC AI conference for developers in Paris (10-12 June 2025), the PCSS’ name appeared among the leading European institutions in the realm of quantum computing during the speech of the NVIDIA co-founder and CEO, Jensen Huang.
Experiments using the largest IBM Q quantum computers
2024-04-14
The Polish Quantum Computing Node established at the Poznań Supercomputing and Networking Center - IBM Quantum Innovation Center - focused its activities in 2023 on expanding partnerships with leading centers and teams dealing with the development of quantum algorithms and their potential applications.






![The image displays the word "LUMEN" in a stylized, outlined font, with different letters connected by lines and arrows to various academic disciplines. The letters "L" and "U" on the left are linked to "Mathematics [Maths]" and "Social Sciences and Humanities [SSH]," while the letters "M," "E," and "N" on the right are associated with "Earth System Science [ESS]" and "Molecular Dynamics [MD]." The overall design suggests an interconnectedness of these fields, potentially illustrating the interdisciplinary nature of something represented by "LUMEN".](https://www.psnc.pl/files/2025/05/lumen2_EN-768x432.jpg)